EV charging infrastructure to emerge as a pillar for the ongoing transition to electric mobility
|
With the
clean energy transition in full swing, EV charging infrastructure
development is becoming paramount in sparking growing acceptance
towards zero-emission vehicles
The
transportation industry has long been one of the main contributors
to CO2 emissions worldwide. In the U.S. alone, the sector accounts
for nearly 28% of carbon emissions, making decarbonization a crucial
undertaking in the journey towards cleaner mobility, with electric
vehicles (EVs) leading the charge.
The EV
revolution has been in the works for a while now and is expected to
continue its growth across the globe over the next decade. According
to the IEA (International Energy Agency)’s 2021 Global Electric
Vehicle Outlook, more than 230 million EVs, equivalent to nearly 12%
of all road transport could be on the streets by 2030.
Despite
several favorable conditions, however, EV adoption still faces some
substantial challenges, most prominently the inadequacy of dedicated
recharging infrastructure. According to a National Renewable Energy
Laboratory study, almost 40 Level 2 and 3.4 DCFC charging points are
required per 1000 EVs. This has spurred many major organizations
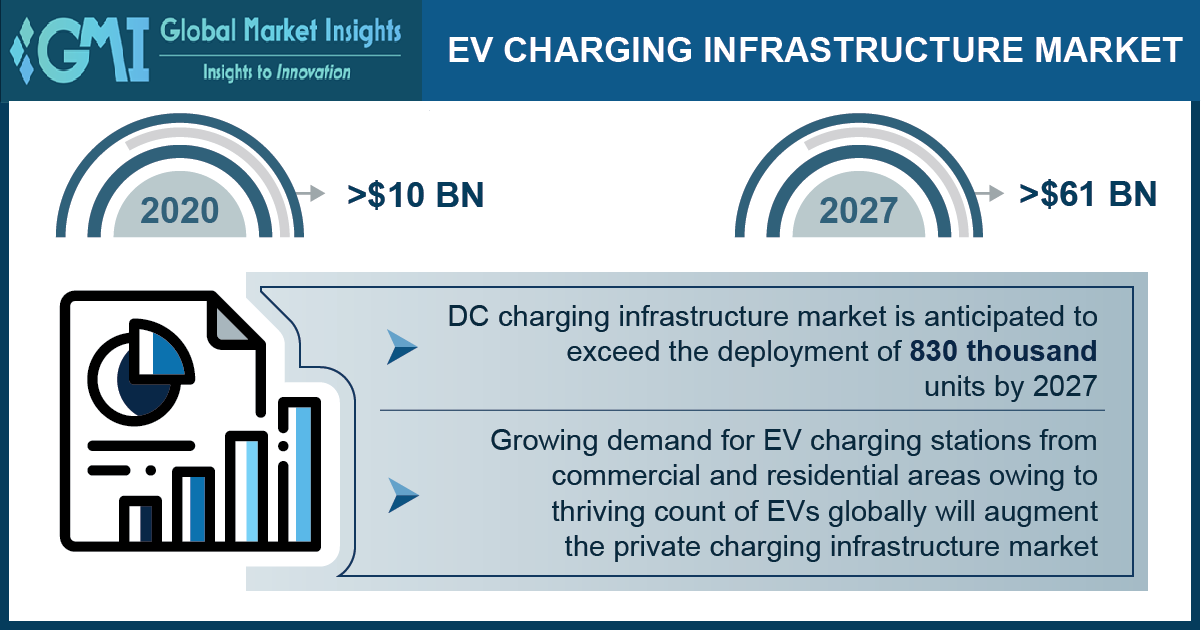
into action, particularly in terms of their contributions to the EV
charging infrastructure market, which is set to cross $61 billion by
2027, according to a Global Market Insights Inc. report.
Public-private sector initiatives promoting EV charging
infrastructure development
In recent
years, several organizations like the IEA have recognized that EV
adoption and its associated economic and ecological benefits are
reliant largely on the availability of dedicated and robust charging
infrastructure.
Range
anxiety, in particular, has been identified as a major roadblock to
the adoption of electric mobility for years, with many EV owners and
prospective buyers becoming apprehensive of the limited availability
of EV charging points. Various entities have started to take
targeted efforts to address these issues, like the U.S. Federal
Government, which in January 2022, unveiled a
$7.5-billion funding plan for a national charging station network
spanning all 50 states.
Designed to
go hand-in-hand with the Biden administration’s Bipartisan
Infrastructure Bill, the funding strategy will support the
government’s plan to convert half of all new car sales into EVs by
2030. Approximately $5 billion will be used to set up charging
points along important transportation corridors, while the remaining
$2.5 billion will help in establishing EV charging ports in small
towns and urban areas, representing a phenomenal boost to the
EV charging infrastructure industry.
Private
sector organizations are not far behind in their EV efforts, which
is evident from the formation of the National Electric Highway
Coalition in December 2021. The coalition, which includes Edison
Electric Institute (EEI) and other major electric companies from
across the U.S. combines the Midwest Electric Vehicle Charging
Infrastructure collaboration and the Electric Highway Coalition.
With the support of an electric cooperative, the Tennessee Valley
Authority and over 51 investor-owned electric firms, the coalition
is determined to develop EV fast-charging points that will boost the
confidence of the public in driving EVs across major travel
corridors in the U.S. by 2030 end.
Simultaneously, efforts are also being taken by entities worldwide
to expedite the transition to electric mobility by installing
charging points as well as converting existing vehicle fleets into
EVs. For instance, the EV100 Initiative by the Climate Group
involves over 100 companies across 80 markets, with the common goal
of establishing EV chargers in over 6,500 locations and switching
over 4.8 million vehicles to electric vehicles, making electric
mobility the new normal by 2030.
EV adoption
garners renewed interest with the emergence of the DC fast charging
era
Despite
certain challenges, EV charging points are gradually becoming more
prevalent across the globe. Most charging points in existence today
are AC chargers, mainly due to their use in home and office
settings, which are considered the most common places to recharge EV
batteries for most drivers. While they allow for more convenience in
EV charging, AC charging points generally require vehicles to be
connected for long periods to reach full charge, which can be
challenging for EV drivers when they are on the move.
In recent
years, however, there has been a surge in the number of public EV
charging infrastructures available, which means that drivers are no
longer restricted to at-home or private stations to recharge their
vehicles. Adding impetus to this are efforts from major companies
that are developing a novel charging technology called DC Fast
Charging, which allows for faster charging of EVs than conventional
AC chargers.
These efforts
are being supported by new initiatives and incentives being put into
place to promote the use of DC EV charging infrastructure. The
Electric Highway Coalition (EHC), for instance, involves a group of
electric utility firms working collaboratively to install EV
fast-charging points along key interstate highways in the United
States. In July 2021, 14 more utilities including DTE Energy,
Eversource Energy, Consolidated Edison, and AVANGRID, among others
joined the coalition, to contribute to the common goal of
accelerating EV adoption.
New York also
made similar efforts in September 2021, by installing
four new EV fast-charging stations at Manhattan-based parking
facility Delancey-Essex Municipal Garage, capable of
charging batteries in most EVs up to 80% in less than 60 minutes.
This was part of the officials’ plan to install 24 additional DC EV
chargers at other municipal garages over the next year, as well as
the city’s broader goal to establish over 80 fast-charging stations
in facilities across five boroughs by 2025 end.
Since the
onset of the EV revolution that began almost a decade ago, there has
been a massive rise in awareness and acceptance worldwide towards
cleaner and more environment-friendly energy alternatives.
Organizations are working hard towards combating air pollution
caused due to existing ICE vehicles, by embracing the gradual
transition to electric mobility. The establishment of advanced and
smarter electric vehicle charging infrastructure is a core part of
this transition, by making EV adoption a lucrative prospect for
businesses and consumers alike in their journey towards a cleaner
future. |